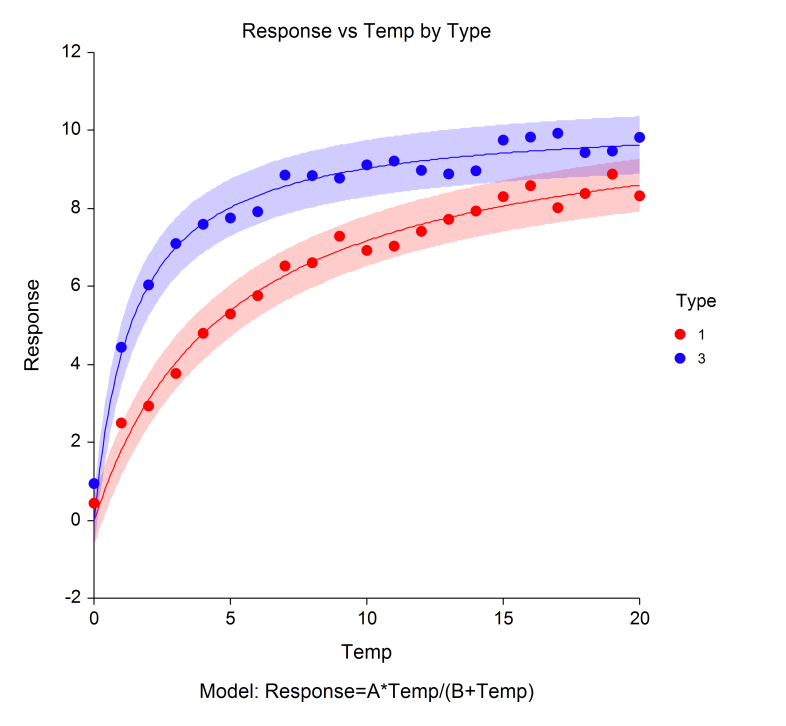
Problem 1
Some computers are equipped with temperatures sensors that monitor various components and activate fans. How does temperature evolve in the parts of a computer after it has been turned on?
Columns: Running time (minutes), CPU A Die (°C), CPU B Die (°C), Memory Controller Heatsink (°C), Drive Bay (°C), "Smart Disk" Hard Drive (°C)
Problem 2
How does specific heat vary with atomic mass? This relationship was first described in 1819 by the French physicists Pierre Louis Dulong (1785–1838) and Aléxis Thérèse Petit (1791–1820) and is now known as the Dulong-Petit law.
Columns: Element name, Atomic mass (atomic mass units), Specific heat capacity (J/kg K)
Source: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 75th Edition. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 1995.
Problem 3
Heinrich Schwabe (1789–1875) was a 19th century astronomer searching for a planet nearer to the Sun than Mercury. He never found this inframercurial planet, but his long term observations of sunspots lead to an important discovery. What was it?
Columns: Year, Number of sunspot clusters, Days when no sunspots were observed, Cloud-free observation days
Source: Sonnen-Beobachtungen im Jahre 1843. Heinrich Schwabe. Astronomische Nachrichten. Vol. 20 No. 495 (1844): 233–236; Kosmos: Entwurf einer physischen Weltbeschreibung, Dritter Band. Alexander von Humboldt. Tübingen, Germany: J.G. Cotta'sche Verlag (1850): 402.
Problem 4
X-rays can be produced by bombarding stationary atoms with a beam of fast moving electrons. The energy of the emerging x-rays peaks around several values, two of which are included in the accompanying text file. x-rays with these peak values are called characteristic x-rays since they can be used to identify elements. How are energy and atomic number related for characteristic x-rays?
Columns: Atomic number, Element, Kα1 (eV), Kα2 (eV)
Source: National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). X-ray Transition Energies Database (2005).
Problem 5
This data set shows the mean orbital radius (in astronomical units) and orbital period (in days or years) of each of the nine planets. Convert the radii to meters, convert the periods to seconds, and then determine the relationship between radius and period. This relationship was discovered in 1619 by the German mathematician Johannes Kepler (1571–1630) and is now known as Kepler's third law of planetary motion. He came to this conclusion 18 years after receiving the data. Given the tools of contemporary analysis, which Kepler did not have access to, you should be able to arrive at a conclusion in under five minutes.
Columns: Planet name, Mean orbital radius in astronomical units (a unit equal to the Earth's orbital radius), Orbital period (Note the change in units between the inner and outer planets.)
Source: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 75th Edition. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 1995.
Problem 6
This file gives the world record times for eight track events.
Calculate the speed of each runner.
Determine…
1. the effect of gender on speed.
2. the effect of distance on speed.
Columns: Event (length in meters), Men's record times (seconds), Women's record times (seconds)
Source: World Athletics
Problem 7
What effect does latitude have on average yearly temperature? Before you attempt this question you must compensate for the variation in altitude of the different data points. Temperature decreases 6.5 °C for every 1,000 m of altitude. Calculate the altitude adjusted temperature for the cities in this data set. If you have done this correctly you will see the correlation of the data set increase. Then perform a curve fit and answer the question.
Columns: City name, Latitude (degrees: positive-north, negative-south), Altitude of recording station (meters), Average yearly temperature (degree Celsius)
Source: worldclimate.com



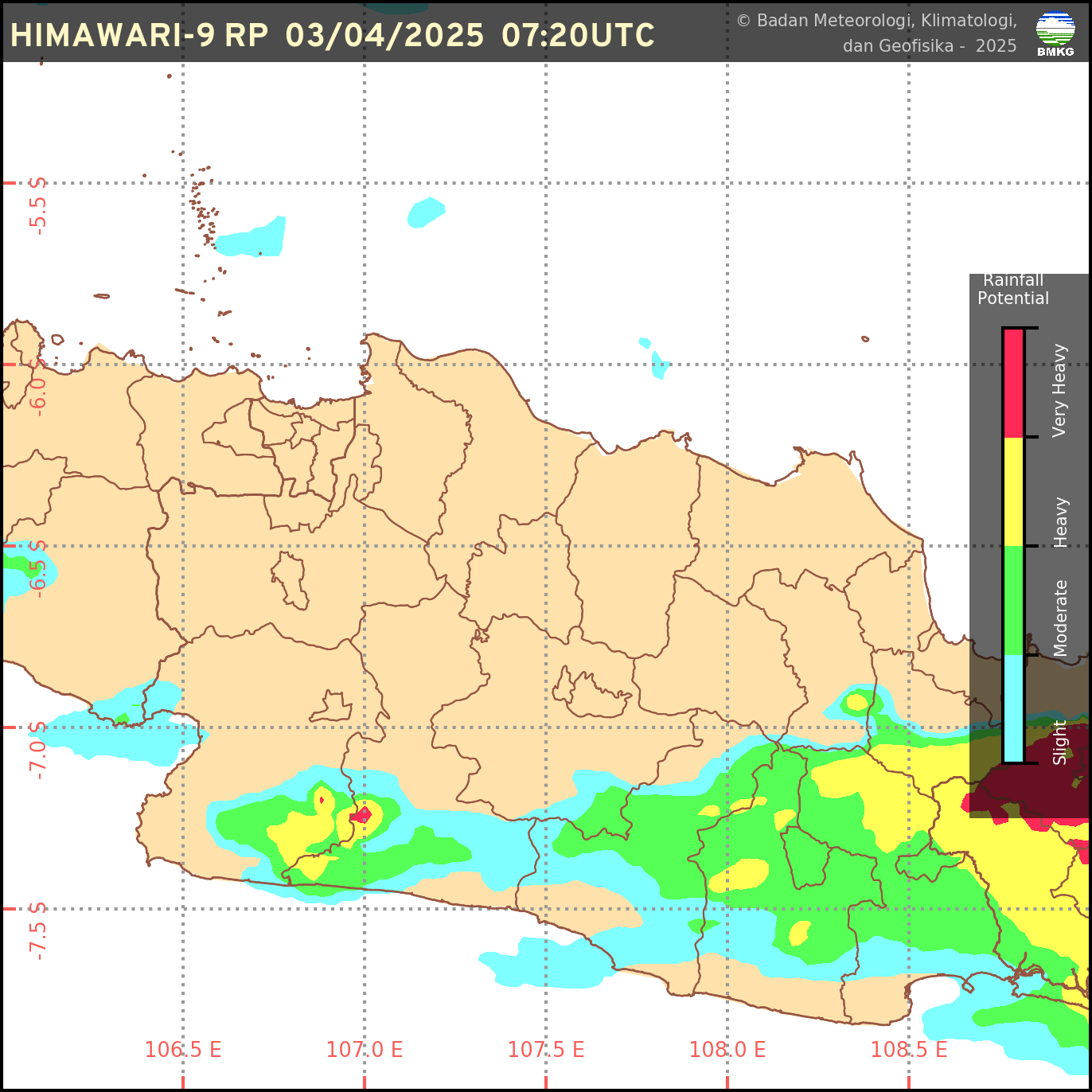 Sumber: BMKG
Sumber: BMKG
1 Komentar
Ryan Pebriansyah - G5401231042 (Hadir)
BalasHapus